
Software engineering is the systematic application of engineering approaches to the development
of software. Software engineering is a computing discipline.
Software is a program or set of programs containing instructions which provide desired
functionality . And Engineering is the processes of designing and building something that serves
a particular purpose and find a cost effective solution to problems.
| As a product | As a vehicle for delivering a product |
|---|---|
| It delivers the computing potential across network of Hardware. | It provides system functionality (e.g., payroll system) |
| It enables the Hardware to deliver the expected functionality. | It controls other software (e.g., an operating system) |
| It acts as information transformer because it produces, manages, acquires, modifies, displays, or transmits information. | It helps build other software (e.g., software tools) |
| Maintainability | It should be feasible for the software to evolve to meet changing requirements. |
|---|---|
| Correctness | A software product is correct, if the different requirements as specified in the SRS document have been correctly implemented |
| Reusability | A software product has good reusability, if the different modules of the product can easily be reused to develop new products. |
| Testability | Here software facilitates both the establishment of test criteria and the evaluation of the software with respect to those criteria. |
| Reliability | It is an attribute of software quality. The extent to which a program can be expected to perform its desired function, over an arbitrary time period. |
| Portability | In this case, software can be transferred from one computer system or environment to another. |
| Adaptability | In this case, software allows differing system constraints and user needs to be satisfied by making changes to the software. |
Software=Program+documentation+licensing.
| Characteristics | Definition | Required functions |
|---|---|---|
| Functionality | It refers to the degree of performance of the software against its intended purpose. |
|
| Reliability | A set of attribute that bear on capability of software to maintain its level of performance under the given condition for a stated period of time. |
|
| Efficiency | It refers to the ability of the software to use system resources in the most effective and efficient manner.the software should make effective use of storage space and executive command as per desired timing requirement. |
|
| Usability | It refers to the extent to which the software can be used with ease.the amount of effort or time required to learn how to use the software. |
|
| Maintainability | It refers to the ease with which the modifications can be made in a software system to extend its functionality, improve its performance, or correct errors. |
|
| Portability | A set of attribute that bear on the ability of software to be transferred from one environment to another, without or minimum changes. |
|
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a process used by the software industry to design, develop and test high quality softwares. The SDLC aims to produce a high-quality software that meets or exceeds customer expectations, reaches completion within times and cost estimates. SDLC is the acronym of Software Development Life Cycle. It is also called as Software Development Process. SDLC is a framework defining tasks performed at each step in the software development process. ISO/IEC 12207 is an international standard for software life-cycle processes. It aims to be the standard that defines all the tasks required for developing and maintaining software.
SDLC is a process followed for a software project, within a software organization. It consists of a detailed plan describing how to develop, maintain, replace and alter or enhance specific software. The life cycle defines a methodology for improving the quality of software and the overall development process.
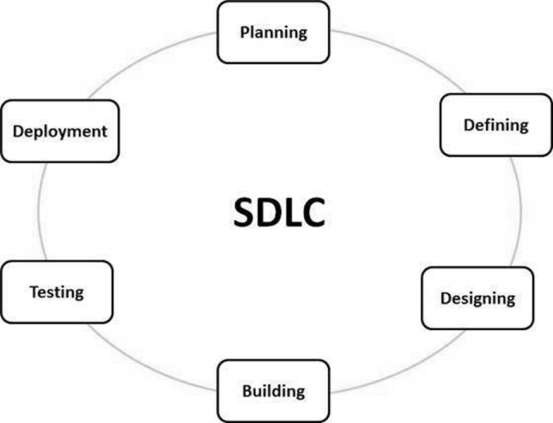
| Planning and Requirement Analysis |
|---|
|
Requirement analysis is the most important and fundamental stage in SDLC. It is
performed by the senior members of the team with inputs from the customer, the
sales department, market surveys and domain experts in the industry. This
information is then used to plan the basic project approach and to conduct
product feasibility study in the economical, operational and technical areas.
Planning for the quality assurance requirements and identification of the risks associated with the project is also done in the planning stage. The outcome of the technical feasibility study is to define the various technical approaches that can be followed to implement the project successfully with minimum risks. |
| Defining Requirements |
| Once the requirement analysis is done the next step is to clearly define and document the product requirements and get them approved from the customer or the market analysts. This is done through an SRS (Software Requirement Specification) document which consists of all the product requirements to be designed and developed during the project life cycle. |
| Designing the Product Architecture |
|
SRS is the reference for product architects to come out with the best
architecture for the product to be developed. Based on the requirements
specified in SRS, usually more than one design approach for the product
architecture is proposed and documented in a DDS - Design Document
Specification.
This DDS is reviewed by all the important stakeholders and based on various parameters as risk assessment, product robustness, design modularity, budget and time constraints, the best design approach is selected for the product. A design approach clearly defines all the architectural modules of the product along with its communication and data flow representation with the external and third party modules (if any). The internal design of all the modules of the proposed architecture should be clearly defined with the minutest of the details in DDS. |
| Building or Developing the Product |
|
In this stage of SDLC the actual development starts and the product is built.
The programming code is generated as per DDS during this stage. If the design is
performed in a detailed and organized manner, code generation can be
accomplished without much hassle.
Developers must follow the coding guidelines defined by their organization and programming tools like compilers, interpreters, debuggers, etc. are used to generate the code. Different high level programming languages such as C, C++, Pascal, Python, Java and PHP are used for coding. The programming language is chosen with respect to the type of software being developed. |
| Testing the Product |
| This stage is usually a subset of all the stages as in the modern SDLC models, the testing activities are mostly involved in all the stages of SDLC. However, this stage refers to the testing only stage of the product where product defects are reported, tracked, fixed and retested, until the product reaches the quality standards defined in the SRS. |
| Deployment in the Market and Maintenance |
|
Once the product is tested and ready to be deployed it is released formally in
the appropriate market. Sometimes product deployment happens in stages as per
the business strategy of that organization. The product may first be released in
a limited segment and tested in the real business environment (UAT- User
acceptance testing).
Then based on the feedback, the product may be released as it is or with suggested enhancements in the targeting market segment. After the product is released in the market, its maintenance is done for the existing customer base. |
There are various software development life cycle models defined and designed which are followed
during the software development process. These models are also referred as Software Development
Process Models". Each process model follows a Series of steps unique to its type to ensure
success in the process of software development.
Following are the most important and popular SDLC models followed in the industry −
Other related methodologies are